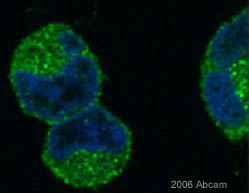
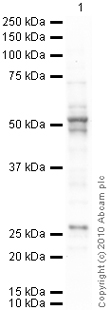
Anti-pan Arrestin antibody
| Name | Anti-pan Arrestin antibody |
|---|---|
| Supplier | Abcam |
| Catalog | ab2914 |
| Prices | $380.00 |
| Sizes | 200 µg |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Applications | ICC/IF ICC/IF WB IHC-P IP |
| Species Reactivities | Rat, Bovine, Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Monkey, Rainbow trout |
| Antigen | Synthetic peptide corresponding to Human pan Arrestin aa 384-397 |
| Description | Rabbit Polyclonal |
| Gene | ARRB1 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Supplier Page | Shop |
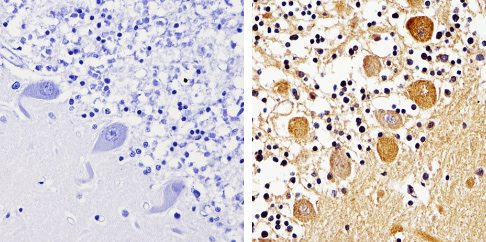
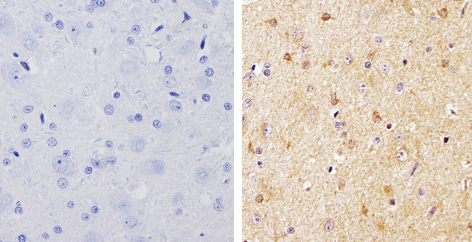
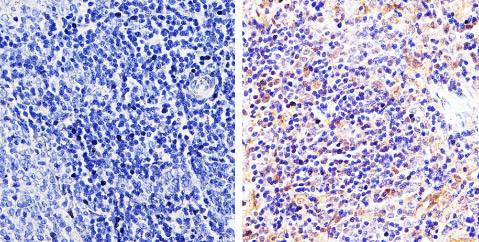
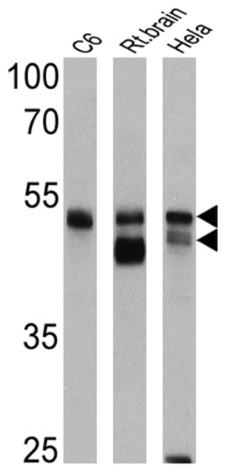
Product images
Product References
Neurotensin-induced proinflammatory signaling in human colonocytes is regulated - Neurotensin-induced proinflammatory signaling in human colonocytes is regulated
Law IK, Murphy JE, Bakirtzi K, Bunnett NW, Pothoulakis C. J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 27;287(18):15066-75.
Beta-arrestin 2 is required for B1 receptor-dependent post-translational - Beta-arrestin 2 is required for B1 receptor-dependent post-translational
Kuhr FK, Zhang Y, Brovkovych V, Skidgel RA. FASEB J. 2010 Jul;24(7):2475-83.
The 27-kDa heat shock protein confers cytoprotective effects through a beta - The 27-kDa heat shock protein confers cytoprotective effects through a beta
Rojanathammanee L, Harmon EB, Grisanti LA, Govitrapong P, Ebadi M, Grove BD, Miyagi M, Porter JE. Mol Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;75(4):855-65.
Intracellular mechanisms regulating corticotropin-releasing hormone - Intracellular mechanisms regulating corticotropin-releasing hormone
Markovic D, Punn A, Lehnert H, Grammatopoulos DK. Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Mar;22(3):689-706. Epub 2007 Nov 29.
Arrestin binds to different phosphorylated regions of the thyrotropin-releasing - Arrestin binds to different phosphorylated regions of the thyrotropin-releasing
Jones BW, Hinkle PM. Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Jul;74(1):195-202.
Targeting of beta-arrestin2 to the centrosome and primary cilium: role in cell - Targeting of beta-arrestin2 to the centrosome and primary cilium: role in cell
Molla-Herman A, Boularan C, Ghossoub R, Scott MG, Burtey A, Zarka M, Saunier S, Concordet JP, Marullo S, Benmerah A. PLoS One. 2008;3(11):e3728.
Platelet-activating factor-induced clathrin-mediated endocytosis requires - Platelet-activating factor-induced clathrin-mediated endocytosis requires
McLaughlin NJ, Banerjee A, Kelher MR, Gamboni-Robertson F, Hamiel C, Sheppard FR, Moore EE, Silliman CC. J Immunol. 2006 Jun 1;176(11):7039-50.