Anti-xCT antibody
| Name | Anti-xCT antibody |
|---|---|
| Supplier | Abcam |
| Catalog | ab37185 |
| Prices | $384.00 |
| Sizes | 100 µl |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Applications | WB FC IHC-P ICC/IF ICC/IF IHC-F |
| Species Reactivities | Mouse, Human |
| Antigen | Synthetic peptide: MVRKPVVSTI SKGGYLQGNV NGRLPSLGNK EPPGQEKVQL , corresponding to N terminal amino acids 1/50 of Human xCT Run BLAST with Run BLAST with |
| Description | Rabbit Polyclonal |
| Gene | SLC7A11 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Supplier Page | Shop |
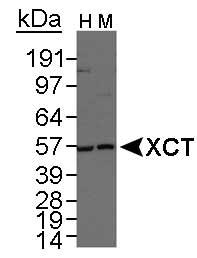
Product images
Product References
Nrf2- and ATF4-dependent upregulation of xCT modulates the sensitivity of T24 - Nrf2- and ATF4-dependent upregulation of xCT modulates the sensitivity of T24
Ye P, Mimura J, Okada T, Sato H, Liu T, Maruyama A, Ohyama C, Itoh K. Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Sep 15;34(18):3421-34.
Suppression of vaccine immunity by inflammatory monocytes. - Suppression of vaccine immunity by inflammatory monocytes.
Mitchell LA, Henderson AJ, Dow SW. J Immunol. 2012 Dec 15;189(12):5612-21.
Increased expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in multiple sclerosis. - Increased expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in multiple sclerosis.
Pampliega O, Domercq M, Soria FN, Villoslada P, Rodriguez-Antiguedad A, Matute C. J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Jun 3;8:63.
Functional induction of the cystine-glutamate exchanger system Xc(-) activity in - Functional induction of the cystine-glutamate exchanger system Xc(-) activity in
Giraudi PJ, Bellarosa C, Coda-Zabetta CD, Peruzzo P, Tiribelli C. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e29078.
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells inhibit T-cell activation by depleting cystine - Myeloid-derived suppressor cells inhibit T-cell activation by depleting cystine
Srivastava MK, Sinha P, Clements VK, Rodriguez P, Ostrand-Rosenberg S. Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 1;70(1):68-77.
HepG2/C3A cells respond to cysteine deprivation by induction of the amino acid - HepG2/C3A cells respond to cysteine deprivation by induction of the amino acid
Lee JI, Dominy JE Jr, Sikalidis AK, Hirschberger LL, Wang W, Stipanuk MH. Physiol Genomics. 2008 Apr 22;33(2):218-29. doi: