
Figure 1: Constitutive phosphorylation of NPM-ALK in Karpas299 cells lysed in the presence of phosphatase inhibitors (phospho-lysate) is detected by PathScan ® Phospho-ALK (Tyr1604) Sandwich ELISA Kit #7324 (top,right). In contrast, only a low level of phospho-NPM-ALK protein is detected in Karpas299 cells lysed without addition of phosphatase inhibitors to the lysis buffer (nonphospho-lysate). However, similar levels of NPM-ALK protein from either nonphospho- or phospho-lysates are detected by PathScan® Total ALK Sandwich ELISA Kit #7322 (top,left). Absorbance at 450 nm is shown in the top figure, while the corresponding western blots using Phospho-ALK (Tyr1604) Antibody #3341 (right) or a Total ALK Rabbit mAb #3337 (left) are shown in the bottom figure. Cell Line Source: Dr Abraham Karpas at the University of Cambridge.
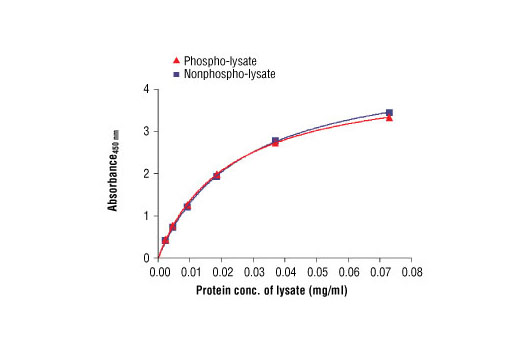
Figure 2: The relationship between protein concentration of phospho- or nonphospho-lysates and the absorbance at 450 nm is shown. Karpas299 cells were harvested at 10 6 cells/ml, and lysed with or without addition of phosphatase inhibitor to the lysis buffer. Cell Line Source: Dr Abraham Karpas at the University of Cambridge.
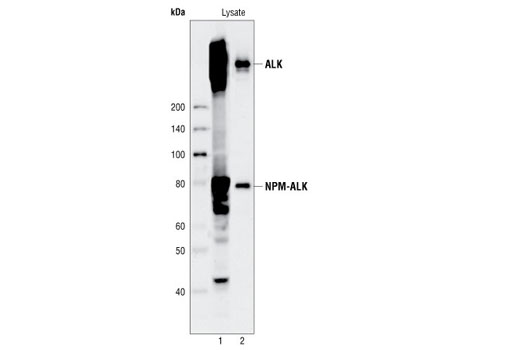
Figure 3. Kit specificity as demonstrated by western analysis of the ELISA microwell captured protein. Human Karpas299 cell lysates were incubated in microwells coated with ALK capture antibody. Following washing, captured protein was solubilized in SDS gel loading buffer. Karpas299 cell lysates (lane 1) and captured protein (lane 2) were analyzed by western blot using the ALK detection antibody. A pair of distinct bands in the captured material (lane 2) correspond to both ALK protein and NPM-ALK fusion protein. Cell Line Source: Dr Abraham Karpas at the University of Cambridge.


