| Description |
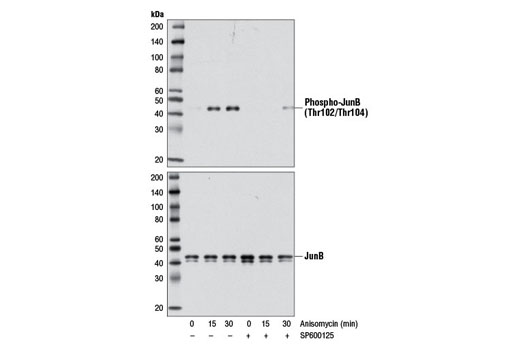
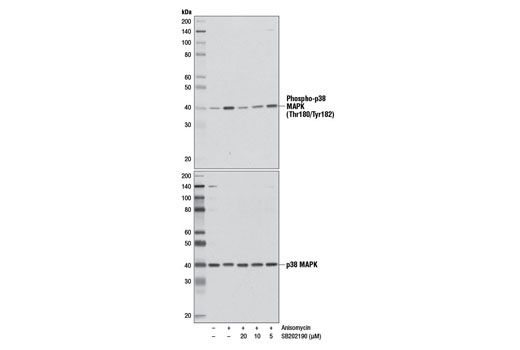
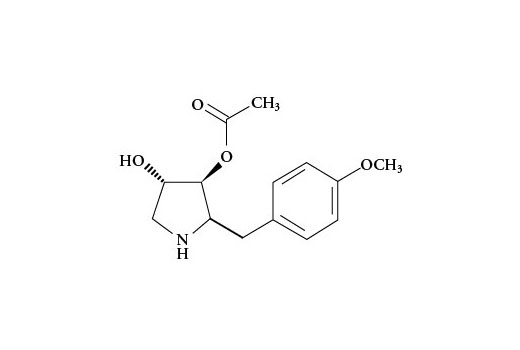
Anisomycin, an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces griseolus and S. roseochromogenes , was originally described to inhibit protein-protein synthesis at the translational level (1). More recently, it is has been well characterized to strongly activate the stress kinases SAPK/JNK and p38 MAPK, as well as p70/85 S6 kinase in mammalian cells, which results in the rapid induction of immediate-early (IE) genes, such as c-fos, fosB, c-jun, JunB, and JunD (1). Investigators have demonstrated that anisomycin acts as a potent signaling agonist, synergizing with growth factors and phorbol esters to superinduce these IE genes (1,2). Research studies have demonstrated that anisomycin induces apoptosis in many cancer cell lines (3-5).
|