| Description |
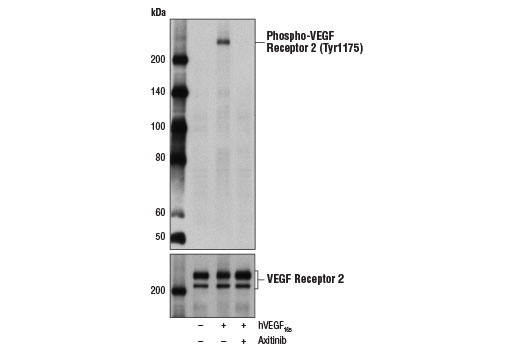
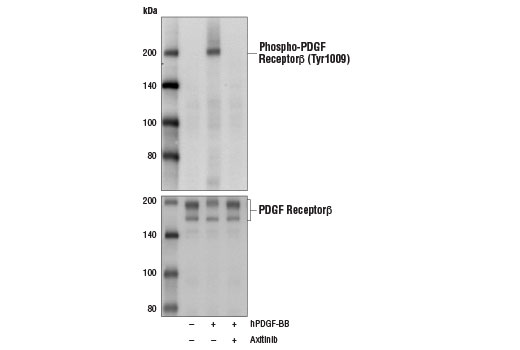
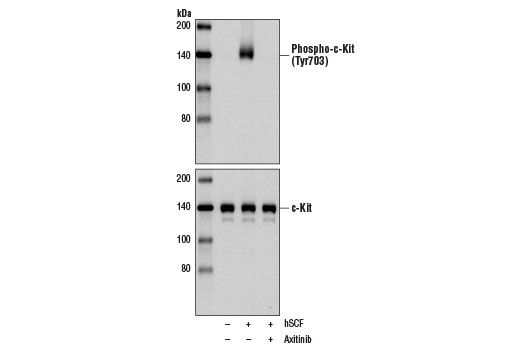
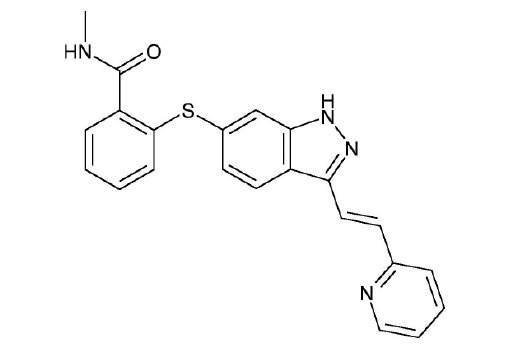
Axitinib is a selective inhibitor of VEGFR, PDGFR, and c-kit tyrosine kinases. Researchers performing cellular phosphorylation assays have shown that axitinib very potently inhibits VEGF-1, -2, and -3 with IC 50 values of approximately 1.2 nM, 0.2 nM, and 0.1-0.3 nM, respectively. It also effectively inhibits PDGF-α (IC 50 = 5.0 nM), PDGF-β (IC 50 = 1.6 nM), and c-kit (IC 50 = 1.7 nM) (1). Axitinib exhibits little activity against a variety of off-target protein kinases when used at 1 µM (1). It inhibits VEGF-induced endothelial cell proliferation, survival, and tube formation, as well as phosphorylation of downstream targets Akt, eNOS, and ERK1/2 in a dose-dependent manner (1). Research studies demonstrate that axitinib suppresses T cell proliferation in a dose dependent manner through G2/M mitotic arrest, while apoptosis is largely prevented though stabilization of Mcl-1 and inactivation of caspase-9 (2). Axitinib has been shown to reduce both hypoxic-induced tissue permeability and overexpression/secretion of VEGF and PDGF in HUVE and RPE cells, as well as alter junction protein expression (3).
|