| Description |
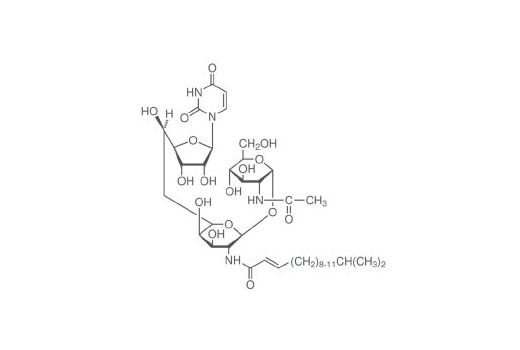
Isolated from Streptomyces lysosuperificus , tunicamycin is a nucleoside antibiotic that inhibits N-linked glycosylation in glycoprotein synthesis. Composed of tunicamycins A, B, C and D, the compound competitively blocks the transfer of N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate (GlcNAc-1-P) from UDP-GlcNAc to dolichol-P (1,2). By preventing glycoprotein synthesis, tunicamycin inhibits the formation of the “viral coat” known as the tunica or capsid in both RNA and DNA viruses, and thus exhibits antiviral properties (3). Research studies have shown that tunicamycin will arrest cells in G1 phase, preventing them from entering S-phase and increasing the expression of PERK (4,5). Following N-linked glycosylation inhibition, tunicamycin induces autophagy in response to ER stress, ultimately upregulating CHOP and BIP (6,7).
|