SignalSilence® DNMT3L siRNA I (Mouse Specific) #12307
Inquiry Info. # 12307
Please see our recommended alternatives.
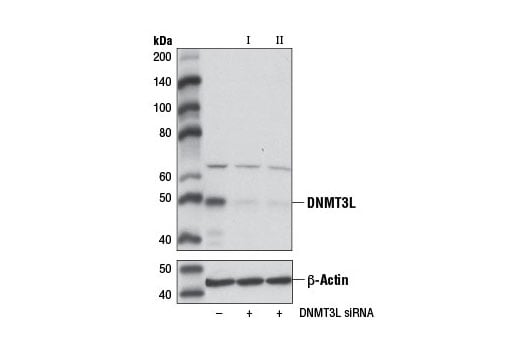
Supporting Data
| REACTIVITY | M |
Species Cross-Reactivity Key:
- M-Mouse
Product Information
Product Usage Information
CST recommends transfection with 100 nM SignalSilence® DNMT3L siRNA I (Mouse Specific) 48 to 72 hours prior to cell lysis. For transfection procedure, follow protocol provided by the transfection reagent manufacturer. Please feel free to contact CST with any questions on use.
Each vial contains the equivalent of 100 transfections, which corresponds to a final siRNA concentration of 100 nM per transfection in a 24-well plate with a total volume of 300 μl per well.
Storage
Product Description
Quality Control
Background
DNMT3L is a catalytically inactive regulatory factor for the DNMT3A and DNMT3B de novo methyltransferases that is expressed at low levels in embryonic stem cells, testis, ovaries, and thymus (1,2). These de novo methyltransferases consist of a heterotetrameric complex containing two molecules of DNMT3L, and either two molecules of DNMT3A or DNMT3B (3). DNMT3L contains an amino-terminal ATRX-DNMT3-DNMT3L (ADD) domain and a carboxy-terminal methyltransferase-like domain (4-7). The methyltransferase-like domain binds to DNMT3A and DNMT3B to stimulate catalytic activity by increasing the binding of S-adenosylmethionine and DNA (4,5). The ADD domain recruits the methyltransferase complex to transcriptionally inactive regions of the genome by binding to unmethylated histone H3 Lys4 (6,7).
- Hermann, A. et al. (2004) Cell Mol Life Sci 61, 2571-87.
- Turek-Plewa, J. and Jagodziński, P.P. (2005) Cell Mol Biol Lett 10, 631-47.
- Jia, D. et al. (2007) Nature 449, 248-51.
- Holz-Schietinger, C. and Reich, N.O. (2010) J Biol Chem 285, 29091-100.
- Suetake, I. et al. (2004) J Biol Chem 279, 27816-23.
- Ooi, S.K. et al. (2007) Nature 448, 714-7.
- Otani, J. et al. (2009) EMBO Rep 10, 1235-41.
Limited Uses
Except as otherwise expressly agreed in a writing signed by a legally authorized representative of CST, the following terms apply to Products provided by CST, its affiliates or its distributors. Any Customer's terms and conditions that are in addition to, or different from, those contained herein, unless separately accepted in writing by a legally authorized representative of CST, are rejected and are of no force or effect.
Products are labeled with For Research Use Only or a similar labeling statement and have not been approved, cleared, or licensed by the FDA or other regulatory foreign or domestic entity, for any purpose. Customer shall not use any Product for any diagnostic or therapeutic purpose, or otherwise in any manner that conflicts with its labeling statement. Products sold or licensed by CST are provided for Customer as the end-user and solely for research and development uses. Any use of Product for diagnostic, prophylactic or therapeutic purposes, or any purchase of Product for resale (alone or as a component) or other commercial purpose, requires a separate license from CST. Customer shall (a) not sell, license, loan, donate or otherwise transfer or make available any Product to any third party, whether alone or in combination with other materials, or use the Products to manufacture any commercial products, (b) not copy, modify, reverse engineer, decompile, disassemble or otherwise attempt to discover the underlying structure or technology of the Products, or use the Products for the purpose of developing any products or services that would compete with CST products or services, (c) not alter or remove from the Products any trademarks, trade names, logos, patent or copyright notices or markings, (d) use the Products solely in accordance with CST Product Terms of Sale and any applicable documentation, and (e) comply with any license, terms of service or similar agreement with respect to any third party products or services used by Customer in connection with the Products.