Anti-IL23 Receptor antibody - Aminoterminal end
| Name | Anti-IL23 Receptor antibody - Aminoterminal end |
|---|---|
| Supplier | Abcam |
| Catalog | ab53656 |
| Prices | $400.00 |
| Sizes | 100 µg |
| Host | Goat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Applications | WB ICC/IF IHC-P |
| Species Reactivities | Mouse, Human, Pig |
| Antigen | Synthetic peptide: CQPRKLHFYKNGIKERFQITRINKTTARL , corresponding to N terminal amino acids 59-87 of Human IL23 Receptor Note: Peptide sequence is <50% identical to other receptors in this region |
| Description | Goat Polyclonal |
| Gene | IL23R |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Supplier Page | Shop |
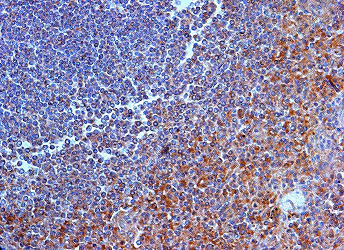
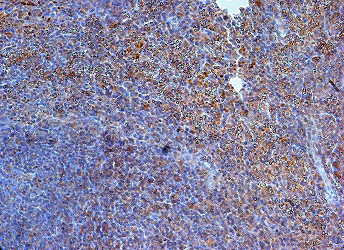
Product images
Product References
IL-23 promotes TCR-mediated negative selection of thymocytes through the - IL-23 promotes TCR-mediated negative selection of thymocytes through the
Li H, Hsu HC, Wu Q, Yang P, Li J, Luo B, Oukka M, Steele CH 3rd, Cua DJ, Grizzle WE, Mountz JD. Nat Commun. 2014 Jul 8;5:4259.
Hepatitis B virus induces IL-23 production in antigen presenting cells and causes - Hepatitis B virus induces IL-23 production in antigen presenting cells and causes
Wang Q, Zhou J, Zhang B, Tian Z, Tang J, Zheng Y, Huang Z, Tian Y, Jia Z, Tang Y, van Velkinburgh JC, Mao Q, Bian X, Ping Y, Ni B, Wu Y. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(6):e1003410.
Morphologic and immunohistochemical characterization of granulomas in the - Morphologic and immunohistochemical characterization of granulomas in the
Janssen CE, Rose CD, De Hertogh G, Martin TM, Bader Meunier B, Cimaz R, Harjacek M, Quartier P, Ten Cate R, Thomee C, Desmet VJ, Fischer A, Roskams T, Wouters CH. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Apr;129(4):1076-84.
Genetic sphingosine kinase 1 deficiency significantly decreases synovial - Genetic sphingosine kinase 1 deficiency significantly decreases synovial
Baker DA, Barth J, Chang R, Obeid LM, Gilkeson GS. J Immunol. 2010 Aug 15;185(4):2570-9.
Induction of Th17 cells in the tumor microenvironment improves survival in a - Induction of Th17 cells in the tumor microenvironment improves survival in a
Gnerlich JL, Mitchem JB, Weir JS, Sankpal NV, Kashiwagi H, Belt BA, Porembka MR, Herndon JM, Eberlein TJ, Goedegebuure P, Linehan DC. J Immunol. 2010 Oct 1;185(7):4063-71.
Heat shock protein-derived T-cell epitopes contribute to autoimmune inflammation - Heat shock protein-derived T-cell epitopes contribute to autoimmune inflammation
Puga Yung GL, Fidler M, Albani E, Spermon N, Teklenburg G, Newbury R, Schechter N, van den Broek T, Prakken B, Billetta R, Dohil R, Albani S. PLoS One. 2009 Nov 2;4(11):e7714.