| Gene Symbol |
MAP2K1
|
| Entrez Gene |
5604
|
| Alt Symbol |
CFC3, MAPKK1, MEK1, MKK1, PRKMK1
|
| Species |
Human
|
| Gene Type |
protein-coding
|
| Description |
mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1
|
| Other Description |
ERK activator kinase 1|MAPK/ERK kinase 1|MAPKK 1|MEK 1|dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1|protein kinase, mitogen-activated, kinase 1 (MAP kinase kinase 1)
|
| Swissprots |
Q02750
|
| Accessions |
EAW77765 EAW77766 EAW77767 EAW77768 EAW77769 Q02750 AK291500 BAF84189 AK294322 BAG57596 AK312356 BC137459 AAI37460 BC139729 AAI39730 BE856741 BG709050 CA419665 DA653983 L05624 AAA36318 L11284 XM_011521783 XP_011520085 NM_002755 NP_002746
|
| Function |
Dual specificity protein kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. Binding of extracellular ligands such as growth factors, cytokines and hormones to their cell-surface receptors activates RAS and this initiates RAF1 activation. RAF1 then further activates the dual-specificity protein kinases MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2. Both MAP2K1/MEK1 and MAP2K2/MEK2 function specifically in the MAPK/ERK cascade, and catalyze the concomitant phosphorylation of a threonine and a tyrosine residue in a Thr-Glu-Tyr sequence located in the extracellular signal-regulated kinases MAPK3/ERK1 and MAPK1/ERK2, leading to their activation and further transduction of the signal within the MAPK/ERK cascade. Depending on the cellular context, this pathway mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation, predominantly through the regulation of transcription, metabolism and cytoskeletal rearrangements. One target of th
|
| Subcellular Location |
Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, spindle pole body. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Note=Localizes at centrosomes during prometaphase, midzone during anaphase and midbody during telophase/cytokinesis.
|
| Tissue Specificity |
Widely expressed, with extremely low levels in brain. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:1281467}.
|
| Top Pathways |
VEGF signaling pathway, Focal adhesion, Gap junction, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
|
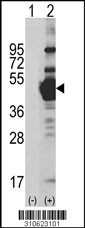
![Western Blot: MEK1 Overexpression Lysate (Adult Normal) [NBL1-12845] Left-Empty vector transfected control cell lysate (HEK293 cell lysate); Right -Over-expression Lysate for MEK1.](http://www.bioprodhub.com/system/product_images/cel_products/5/sub_2/6312_MEK1%2520Overexpression%2520Lysate%2520(Adult%2520Normal)-Western%2520Blot-NBL1-12845-img0002.jpg)