| Gene Symbol |
CIDEC
|
| Entrez Gene |
63924
|
| Alt Symbol |
CIDE-3, CIDE3, FPLD5, FSP27
|
| Species |
Human
|
| Gene Type |
protein-coding
|
| Description |
cell death-inducing DFFA-like effector c
|
| Other Description |
cell death activator CIDE-3|fat specific protein 27
|
| Swissprots |
Q67DW9 C9JMN7 Q9GZY9 Q96AQ7
|
| Accessions |
CAC09160 EAW64011 EAW64012 EAW64013 EAW64014 Q96AQ7 AF303893 AAN32612 AK024524 BAB14920 AK024530 BAB14922 AL598630 AL598731 AY364638 AAR23106 AY364640 AAQ65242 BC016851 AAH16851 CD518729 CD519587 HQ447102 ADQ31589 XM_005265374 XP_005265431 XM_005265375 XP_005265432 XM_005265376 XP_005265433 NM_001199551 NP_001186480 NM_001199552 NP_001186481 NM_001199623 NP_001186552 NM_022094 NP_071377
|
| Function |
Binds to lipid droplets and regulates their enlargement, thereby restricting lipolysis and favoring storage. At focal contact sites between lipid droplets, promotes directional net neutral lipid transfer from the smaller to larger lipid droplets. The transfer direction may be driven by the internal pressure difference between the contacting lipid droplet pair. Its role in neutral lipid transfer and lipid droplet enlargement is activated by the interaction with PLIN1. May act as a CEBPB coactivator in the white adipose tissue to control the expression of a subset of CEBPB downstream target genes, including SOCS1, SOCS3, TGFB1, TGFBR1, ID2 and XDH. When overexpressed in preadipocytes, induces apoptosis or increases cell susceptibility to apoptosis induced by serum deprivation or TGFB treatment. As mature adipocytes, that express high CIDEC levels, are quite resistant to apoptotic stimuli, the physiological significance of its role in apoptosis is unclear. May play a role in the modulatio
|
| Subcellular Location |
Nucleus {ECO:0000250}. Endoplasmic reticulum. Lipid droplet. Note=Diffuses quickly on lipid droplet surface, but becomes trapped and clustered at lipid droplet contact sites, thereby enabling its rapid enrichment at lipid droplet contact sites.
|
| Tissue Specificity |
Expressed mainly in adipose tissue, small intestine, heart, colon and stomach and, at lower levels, in brain, kidney and liver. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12429024, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18334488}.
|
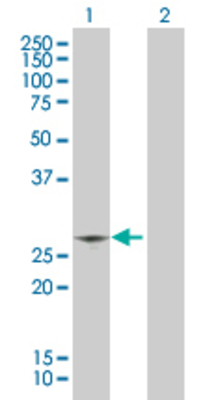
![Western Blot: CIDEC Overexpression Lysate (Adult Normal) [NBL1-09207] Left-Empty vector transfected control cell lysate (HEK293 cell lysate); Right -Over-expression Lysate for CIDEC.](http://www.bioprodhub.com/system/product_images/cel_products/5/sub_2/4254_CIDEC%2520Overexpression%2520Lysate%2520(Adult%2520Normal)-Western%2520Blot-NBL1-09207-img0002.jpg)