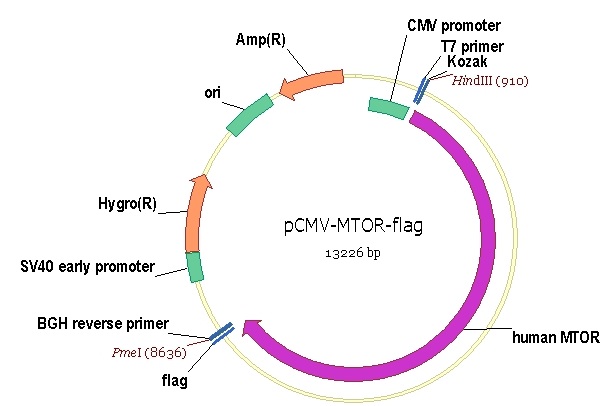
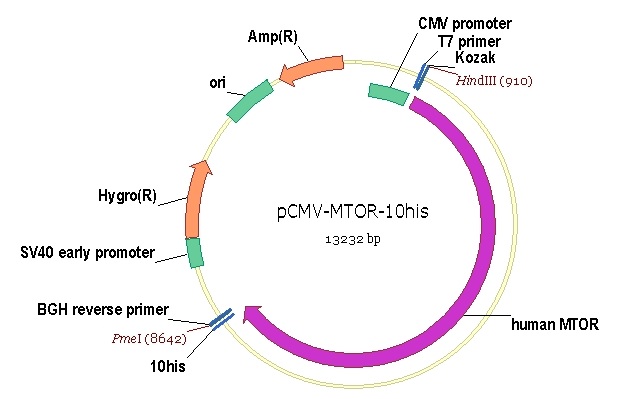
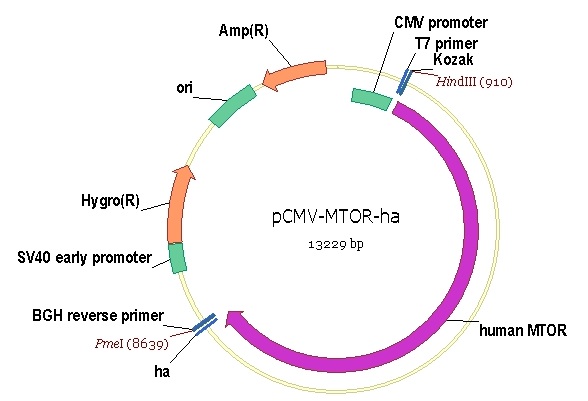
MTOR
| Gene Symbol | MTOR |
|---|---|
| Entrez Gene | 2475 |
| Alt Symbol | FRAP, FRAP1, FRAP2, RAFT1, RAPT1 |
| Species | Human |
| Gene Type | protein-coding |
| Description | mechanistic target of rapamycin (serine/threonine kinase) |
| Other Description | FK506 binding protein 12-rapamycin associated protein 2|FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin complex-associated protein 1|FKBP-rapamycin associated protein|FKBP12-rapamycin complex-associated protein 1|mammalian target of rapamycin|rapamycin and FKBP12 target 1|rapamycin associated protein FRAP2|rapamycin target protein 1|serine/threonine-protein kinase mTOR |
| Swissprots | P42345 Q96QG3 Q4LE76 Q6LE87 Q5TER1 Q9Y4I3 |
| Accessions | CAC15570 CAC42395 CCW44092 EAW71681 EAW71682 EAW71683 P42345 AA725390 AB209995 BAE06077 AK126762 BAG54371 AK302863 BAG64047 AK304273 BAG65134 BC117166 AAI17167 BP250183 DC403129 L34075 AAA58486 L35478 AAC41713 U88966 AAC39933 XM_005263438 XP_005263495 XM_011541166 XP_011539468 XR_244786 NM_004958 NP_004949 |
| Function | Serine/threonine protein kinase which is a central regulator of cellular metabolism, growth and survival in response to hormones, growth factors, nutrients, energy and stress signals. MTOR directly or indirectly regulates the phosphorylation of at least 800 proteins. Functions as part of 2 structurally and functionally distinct signaling complexes mTORC1 and mTORC2 (mTOR complex 1 and 2). Activated mTORC1 up-regulates protein synthesis by phosphorylating key regulators of mRNA translation and ribosome synthesis. This includes phosphorylation of EIF4EBP1 and release of its inhibition toward the elongation initiation factor 4E (eiF4E). Moreover, phosphorylates and activates RPS6KB1 and RPS6KB2 that promote protein synthesis by modulating the activity of their downstream targets including ribosomal protein S6, eukaryotic translation initiation factor EIF4B, and the inhibitor of translation initiation PDCD4. Stimulates the pyrimidine biosynthesis pathway, both by acute regulation through R |
| Subcellular Location | Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Golgi apparatus membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Mitochondrion outer membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Lysosome. Cytoplasm {ECO:0000250}. Nucleus, PML body {ECO:0000250}. Note=Shuttles between cytoplasm and nucleus. Accumulates in the nucleus in response to hypoxia (By similarity). Targeting to lysosomes depends on amino acid availability and RRAGA and RRAGB. {ECO:0000250}. |
| Tissue Specificity | Expressed in numerous tissues, with highest levels in testis. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12408816, ECO:0000269|PubMed:7809080}. |
| Top Pathways | Proteoglycans in cancer, AMPK signaling pathway, Central carbon metabolism in cancer, Choline metabolism in cancer, MicroRNAs in cancer |
Search more