| Gene Symbol |
EGLN1
|
| Entrez Gene |
54583
|
| Alt Symbol |
C1orf12, ECYT3, HALAH, HIF-PH2, HIFPH2, HPH-2, HPH2, PHD2, SM20, ZMYND6
|
| Species |
Human
|
| Gene Type |
protein-coding
|
| Description |
egl-9 family hypoxia-inducible factor 1
|
| Other Description |
HIF prolyl hydroxylase 2|HIF-prolyl hydroxylase 2|egl nine homolog 1|egl nine-like protein 1|hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase 2|prolyl hydroxylase domain-containing protein 2|zinc finger MYND domain-containing protein 6
|
| Swissprots |
Q9BZS8 Q9GZT9 Q8N3M8 Q9BZT0
|
| Accessions |
AAG34568 AFM52328 AGL94896 AGL94897 AGL94898 AGL94899 AGL94900 AGL94901 AGL94902 AGL94903 AGL94904 AGL94905 AGL94906 AGL94907 AGL94908 AGL94909 AGL94910 AGL94911 AGL94912 AGL94913 AGL94914 AGL94915 AGL94916 AGL94917 AGL94918 AGL94919 AGL94920 AGL94921 AGL94922 AGL94923 AGL94924 AGL94925 AGL94926 AGL94927 AGL94928 AGL94929 AGL94930 AGL94931 AGL94932 AGL94933 AGL94934 AGL94935 AGL94936 AGL94937 AGL94938 AGL94939 AGL94940 AGL94941 CAP11376 CDM55390 CDM55571 EAW69959 Q9GZT9 AF229245 AAG33965 AF277174 AAK07534 AF277176 AAK07536 AF334711 AI017372 AJ227859 AJ310543 CAC42509 AL833885 CAD38741 BC005369 AAH05369 DQ975380 ABM44413 XM_005273166 XP_005273223 XM_005273167 XP_005273224 NM_022051 NP_071334
|
| Function |
Cellular oxygen sensor that catalyzes, under normoxic conditions, the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) alpha proteins. Hydroxylates a specific proline found in each of the oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) domains (N-terminal, NODD, and C-terminal, CODD) of HIF1A. Also hydroxylates HIF2A. Has a preference for the CODD site for both HIF1A and HIF1B. Hydroxylated HIFs are then targeted for proteasomal degradation via the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex. Under hypoxic conditions, the hydroxylation reaction is attenuated allowing HIFs to escape degradation resulting in their translocation to the nucleus, heterodimerization with HIF1B, and increased expression of hypoxy-inducible genes. EGLN1 is the most important isozyme under normoxia and, through regulating the stability of HIF1, involved in various hypoxia-influenced processes such as angiogenesis in retinal and cardiac functionality. Target proteins are preferencially recogniz
|
| Subcellular Location |
Cytoplasm {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12615973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19339211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19631610}. Nucleus {ECO:0000269|PubMed:12615973, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19339211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19631610}. Note=Mainly cytoplasmic. Shuttles between the nucleus and cytoplasm (PubMed:19631610). Nuclear export requires functional XPO1. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:19339211, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19631610}.
|
| Tissue Specificity |
According to PubMed:11056053, widely expressed with highest levels in skeletal muscle and heart, moderate levels in pancreas, brain (dopaminergic neurons of adult and fetal substantia nigra) and kidney, and lower levels in lung and liver. According to PubMed:12351678 widely expressed with highest levels in brain, kidney and adrenal gland. Expressed in cardiac myocytes, aortic endothelial cells and coronary artery smooth muscle. According to PubMed:12788921; expressed in adult and fetal heart, brain, liver, lung, skeletal muscle and kidney. Also expressed in placenta. Highest levels in adult heart, brain, lung and liver and fetal brain, heart spleen and skeletal muscle. {ECO:0000269|PubMed:11056053, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12163023, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12351678, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12670503, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12788921}.
|
| Top Pathways |
Renal cell carcinoma
|
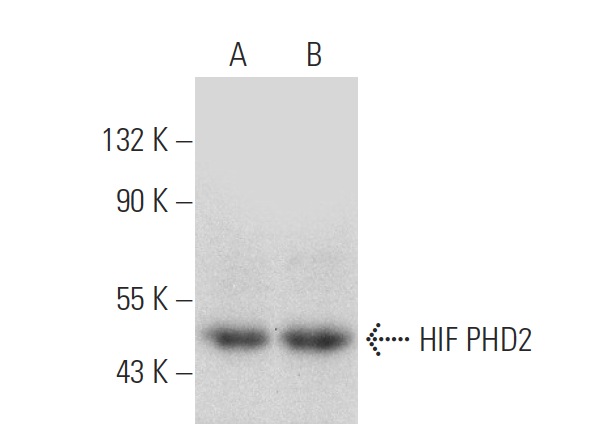
![Overlay histogram showing SHSY-5Y cells stained with ab103432 (red line). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (10 min) and then permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Tween for 20 min. The cells were then incubated in 1x PBS / 10% normal goat serum / 0.3M glycine to block non-specific protein-protein interactions followed by the antibody (ab103432, 0.1μg/1x106 cells) for 30 min at 22°C. The secondary antibody used was Alexa Fluor® 488 goat anti-mouse IgG (H&L) (ab150113) at 1/2000 dilution for 30 min at 22°C. Isotype control antibody (black line) was mouse IgG1 [ICIGG1] (ab91353, 1μg/1x106 cells) used under the same conditions. Unlabelled sample (blue line) was also used as a control. Acquisition of >5,000 events were collected using a 20mW Argon ion laser (488nm) and 525/30 bandpass filter. This antibody gave a positive signal in SHSY-5Y cells fixed with 80% methanol (5 min)/permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Tween for 20 min used under the same conditions.](http://www.bioprodhub.com/system/product_images/ab_products/2/sub_4/10866_ab103432-1-ab103432FC.jpg)
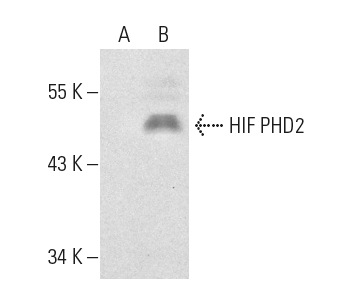
![Anti-PHD2 / prolyl hydroxylase antibody [AT1E9] (ab100840) at 1/1000 dilution + HeLa cell lysate at 35 µgSecondaryHRP conjugated goat anti-mouse developed using the ECL technique](http://www.bioprodhub.com/system/product_images/ab_products/2/sub_4/10867_PHD2-prolyl-hydroxylase-Primary-antibodies-ab100840-2.jpg)
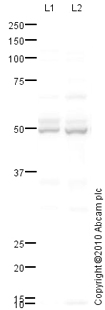
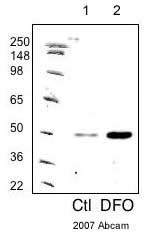
![All lanes : Anti-PHD2 / prolyl hydroxylase antibody [EPR3660(B)(2)] (ab133630) at 1/1000 dilutionLane 1 : SH-SY5Y cell lysate treated with cobalt chlorideLane 2 : SH-SY5Y cell lysateLane 3 : Human adrenal gland lysateLysates/proteins at 10 µg per lane.SecondaryHRP labelled goat anti-rabbit at 1/2000 dilution](http://www.bioprodhub.com/system/product_images/ab_products/2/sub_4/10869_PHD2-prolyl-hydroxylase-Primary-antibodies-ab133630-1.jpg)
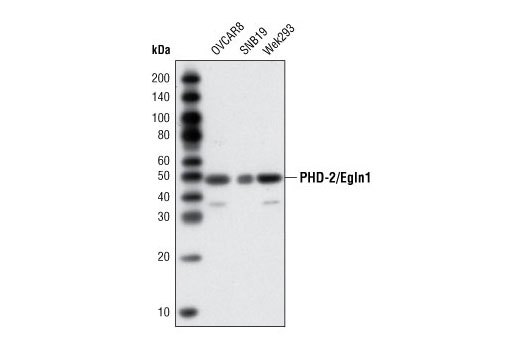
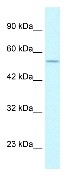
![All lanes : Anti-PHD2 / prolyl hydroxylase antibody [mAbcam74796] (ab74796) at 5 µg/mlLane 1 : Skeletal Muscle (Human) Tissue Lysate - adult normal tissue (ab29330)Lane 2 : HepG2 (Human hepatocellular liver carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate Lane 3 : HeLa (Human epithelial carcinoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate Lane 4 : U2OS (Human osteosarcoma cell line) Whole Cell Lysate Lysates/proteins at 10 µg per lane.SecondaryGoat polyclonal to Mouse IgG - H&L - Pre-Adsorbed (HRP) at 1/3000 dilutiondeveloped using the ECL techniquePerformed under reducing conditions.](http://www.bioprodhub.com/system/product_images/ab_products/2/sub_4/10875_PHD2-prolyl-hydroxylase-Primary-antibodies-ab74796-1.jpg)